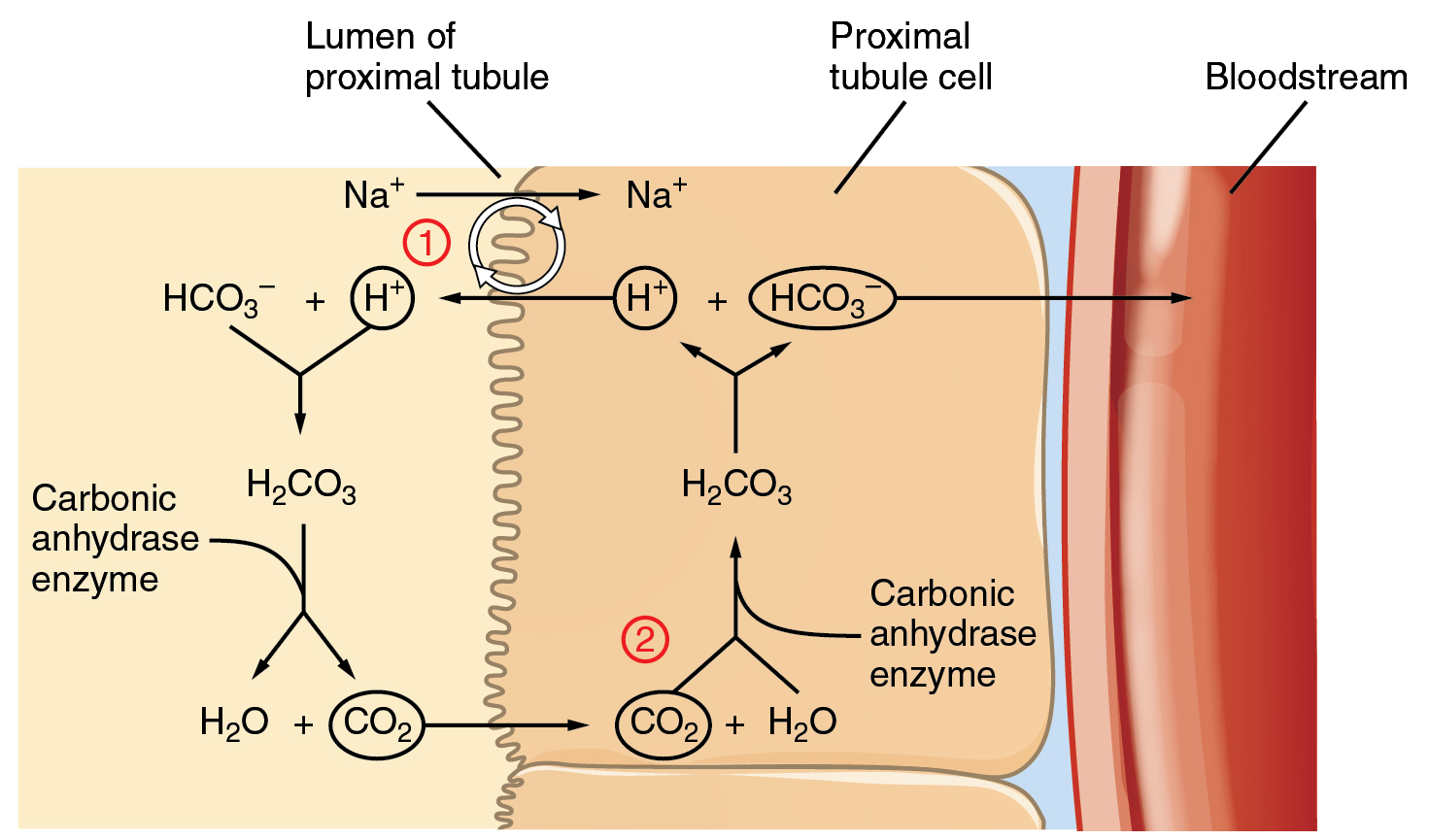
Working along the nephron …
PRE-RENAL
- antihypertensives
diuretics
SMALL VESSEL DISEASE
Haemodynamic
- NSAIDs
ACE-I, ARBs
radio-contrast
cyclosporin, tacrolimus
noradrenaline, cocaine
Thrombotic microangiopathic
- cyclosporin, tacrolimus
mitomycin C
clopidogrel
quinine
oral contraceptives
GLOMERULAR DISEASE
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
- D-penicillamine
hydralazine
propylthiouracil
organic solvents
silica compounds
amphetamines
ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS
- amphotericin
aminoglycosides
cisplatin
ifosfamide
paracetamol
heavy metals
herbal remedies
radio-contrast agents
pentamide
organic solvents
herbicides (paraquat)
intravenous immunoglobulin
INTRATUBULAR OBSTRUCTION
- crystal formation
acyclovir
ethylene glycol
sulphonamide antibiotics
methotrexate
indinavir
triamterene
ACUTE ALLERGIC INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS
- Proton-pump inhibitors
Antibiotcs – penicillins, cephalosporins, rifampicin, sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin
NSAIDs
Loop and thiazide diuretics
allopurinol
cimetidine
mesalazine
analgesics
POST-RENAL OBSTRUCTION
- Papillary necrosis – NSAIDs, compound analgesics
Urinary retention – anticholinergics, tricyclic antidepressants
 |
| For clarity, blood vessels not shown |
Like this:
Like Loading...
Related
Published by Son of Pilgrim
"May The Lord bless thee, and keep thee: The Lord make his face shine upon thee, and be gracious unto thee: The Lord lift up his countenance upon thee, and give thee peace."
View all posts by Son of Pilgrim